Table of Contents
Beginners Level Software Testing Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
1. What are the phases involved in Software Testing Life Cycle?
The different phases involved in the software testing life cycle are:
2. What are the different methods of testing?
There are three methods of software testing and they are as follows:
- Black-box testing: It is a testing strategy based solely on requirements and specifications. In this strategy, it requires no knowledge of internal paths, structures, or implementation of the software being tested.
- White box testing: It is a testing strategy based on internal paths, code structures, and implementation of the software being tested. White box testing generally requires detailed programming skills.
- Gray box testing: It is a strategy for software debugging in which the tester has limited knowledge of the internal details of the program.
3. What are the different levels of testing?
There are mainly four testing levels and they are:
Basically, it starts with the Unit Testing phase and ends with Acceptance Testing.
4. Explain Bug Life Cycle or Defect life cycle.
A defect life cycle is a process in which a defect goes through various phases during its entire lifetime. It starts when a defect is found and ends when a defect is closed, after ensuring it’s not reproduced.
Bug or defect life cycle includes the steps as illustrated in the below figure. If you wish to learn in depth about Bug Life Cycle then you can refer my article on Software Testing Tutorial.
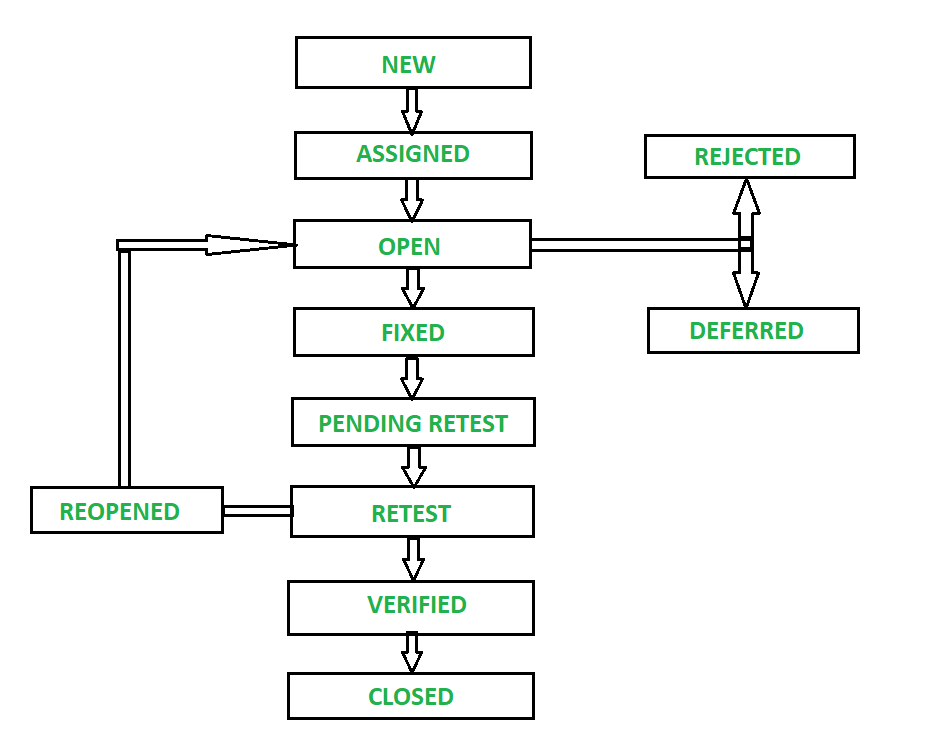
It can vary from organization to organization and also from project to project based on several factors like organization policy, software development model used (like Agile, Iterative), project timelines, team structure etc.
5. What is a test case?
A test case is nothing but a set of conditions or variables under which a tester will determine whether a system under test satisfies requirements or works correctly.
6. What is the difference between functional and non-functional testing?
| Functional Testing | Non Functional Testing |
Performed before non-functional testing | Performed after functional testing |
Based on customers expectations | |
Describes what the product does | Describes how the product works |
7. What is Verification and Validation in Software Testing?
Verification: It is a static analysis technique. Here, testing is done without executing the code. Examples include – Reviews, Inspection, and walkthrough.
Validation: It is a dynamic analysis technique where testing is done by executing the code. Examples include functional and non-functional testing techniques.
In the V model, the development and QA activities are done simultaneously. There is no discrete phase called Testing, rather testing starts right from the requirement phase. The verification and validation activities go hand in hand.
8. What is usability testing?
It is a testing methodology where the end customer is asked to use the software to see if the product is easy to use, to see the customer’s perception and task time. An accurate way to finalize the customer point of view for usability is by using prototype or mock-up software during the initial stages.
9. What are the categories of defects?
There are three main categories of defects :
- Wrong: It implies that requirements have been implemented incorrectly. It is a variance from the given specification.
- Missing: This is a variance from the specifications, an indication that a specification was not implemented, or a requirement of the customer was not noted properly.
- Extra: It is a requirement incorporated into the product that was not given by the end customer. It is always a variance from the specification but may be an attribute desired by the user of the product.
10. On what basis the acceptance plan is prepared?
Basically, the acceptance document is prepared using the following inputs.
- Requirement document: It specifies what exactly is needed in the project from the customers perspective.
- Input from the customer: This can be discussions, informal talks, emails, etc.
- Project plan: The project plan prepared by the project manager also serves as good input to finalize your acceptance test.
11. What is coverage and what are the different types of coverage techniques?
The parameter used in software testing to describe the extent to which the source code is tested is known as coverage. There are three basic types of coverage techniques and they are:
- Statement coverage: It ensures that each line of source code has been executed and tested.
- Decision coverage: It assures that every decision (true/false) in the source code has been executed and tested.
- Path coverage: Here we ensure that every possible route through a given part of the code is executed and tested.
12. What are the benefits of Automation testing?
Benefits of Automation testing are:
- Supports execution of repeated test cases
- Aids in testing a large test matrix
- Enables parallel execution
- Encourages unattended execution
- Improves accuracy thereby reducing human-generated errors
- Saves time and money
13. Why Selenium is a preferred tool for Automation testing?
Selenium is an open source tool which is used for automating the tests carried out on web browsers. Since Selenium is open-source, there is no licensing cost involved, which is a major advantage over other testing tools. Other reasons behind Selenium’s ever-growing popularity are:
- Test scripts can be written in any of these programming languages: Java, Python, C#, PHP, Ruby, Perl &.Net
- Tests can be carried out in any of these OS: Windows, Mac or Linux
- Tests can be carried out using any browser: Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Safari or Opera
- It can be integrated with tools such as TestNG & JUnit for managing test cases and generating reports
- It can be integrated with Maven, Jenkins & Docker to achieve Continuous Testing
14. What are the various components of Selenium?
Different components of Selenium are:
- Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
- Selenium Remote Control (RC)
- Selenium WebDriver
- Selenium Grid
15. What are the different types of locators in Selenium?
The locator is nothing but an address that identifies a web element uniquely within the webpage. Thus, to identify web elements accurately and precisely we have different types of locators in Selenium as follows:
- ID
- ClassName
- Name
- TagName
- linkText
- PartialLinkText
- Xpath
- CSS Selector
- DOM
16. What is XPath?
XPath also called as XML Path is a language to query XML documents. It is an important strategy to locate elements in selenium. It consists of a path expression along with some conditions. Here, you can easily write XPath script/query to locate any element in the webpage. It is designed to allow the navigation of XML documents, with the purpose of selecting individual elements, attributes, or some other part of an XML document for specific processing. It also produces reliable locators.
17. What is the difference between Absolute and Relative Path?
- Absolute XPath
It is the direct way to find the element, but the disadvantage of the absolute XPath is that, if there are any changes made in the path of the element then that XPath gets failed. For example: /html/body/div[1]/section/div[1]/div
- Relative XPath
For Relative XPath, the path starts from the middle of the HTML DOM structure. It begins with the double forward slash (//), which means it can search the element anywhere at the webpage. For example: //input[@id=‘ap_email’]
18. What are the different exceptions in Selenium WebDriver?
Exceptions in Selenium are similar to exceptions in other programming languages. The most common exceptions in Selenium are:
- TimeoutException
- NoSuchElementException
- ElementNotVisibleException
- StaleElementException
19. When should I use Selenium Grid?
Selenium Grid can be used to execute same or different test scripts on multiple platforms and browsers concurrently so as to achieve distributed test execution, testing under different environments and saving execution time remarkably.
20. How do I launch the browser using WebDriver?
The following syntax can be used to launch the Browser:
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
WebDriver driver = new InternetExplorerDriver();
.
























